Get a detailed overview of the CTET Exam Pattern 2026, including Paper I & II structure, subject-wise weightage, marking scheme, and qualifying criteria. Prepare effectively for CTET 2026 with the latest exam format and guidelines.
The CTET Exam 2026 is a national-level examination conducted by the Central Board of Secondary Education in India. It serves as a qualifying criterion for candidates aspiring to become teachers in central government schools such as Kendriya Vidyalayas and Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalayas. Understanding the CTET exam pattern 2026 is crucial for effective preparation. Below is a comprehensive overview of the CTET Exam Pattern for 2026.
CTET Exam Pattern 2026 Overview
The CTET Exam 2026 consists of MCQ with a total of 150 questions in both Paper I and Paper II. Each correct answer carries one mark, and there is no negative marking for incorrect or unattempted answers. The exam will be conducted in offline mode.
| Details | Paper 1 | Paper 2 |
| Mode of Exam | Offline – Pen and Paper Based | Offline – Pen and Paper Based |
| Exam Duration | 2.5 Hours | 2.5 Hours |
| Total Questions | 150 | 150 |
| Total Marks | 150 | 150 |
| Exam Language | English and Hindi | English and Hindi |
| Question Type | Multiple-choice questions (MCQs) | Multiple-choice questions (MCQs) |
| Marking Scheme | Correct Answer: +1 | Correct Answer: +1 |
| Negative Marking | No | No |
CTET Exam Pattern 2026 PAPER 1
CTET Exam 2026 Paper I is conducted for candidates who wish to teach primary level students Classes I-V. The exam consists of five sections, with each section carrying 30 questions for 30 marks, making a total of 150 questions for 150 marks.
CTET Paper I Exam Pattern
| Subject | Topics | Weightage |
| Child Development & Pedagogy | Inclusive Education, Learning, Pedagogy & Development | 30 Marks |
| Language I | Pedagogy of Language Development, Comprehension | 30 Marks |
| Language II | Pedagogy of Language Development, Comprehension | 30 Marks |
| Mathematics | Algebra, Pedagogical Issues, Numbers, Geometry | 30 Marks |
| Environmental Studies | Environment, Pedagogical Issues, Water, Family | 30 Marks |
CTET Exam Pattern 2026 PAPER 2
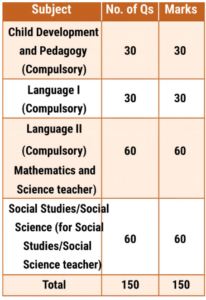
CTET Exam 2026 Paper II is designed for candidates who wish to teach upper primary students Classes VI-VIII. It consists of four sections, including a subject-specific choice between Mathematics & Science or Social Studies.
CTET Paper II Exam Pattern
| Subject | Topics | Weightage |
| Child Development & Pedagogy | Child Development, Pedagogical Issues, Learning Theories, | 30 Marks |
| Language I | Comprehension, Pedagogy | 30 Marks |
| Language II | Comprehension, Pedagogy | 30 Marks |
| Mathematics & Science OR Social Studies | Mathematics, Pedagogical Issues, Science, Social Studies | 60 Marks |
- The total exam duration is 2.5 hours.
- The exam is conducted offline.
- Candidates must choose between Mathematics & Science or Social Studies.
How to Check the CTET Exam Pattern 2026
Candidates can download the CTET exam pattern 2026 from the official website. The candidates can also take a look at the following steps through which they can download the CTET exam pattern 2026.
Step 1 Go to the official website of the CTET https://ctet.nic.in/
Step 2 On the homepage, click on the ‘Information’ section.
Step 3 Now, look for the link for information bulletin and click on it
Step 4 With this, a new PDF will open which will consist of CTET 2026 exam notification
Step 5 In the same PDF, candidates will be able to find the CTET Exam Pattern 2026.
Also Read: CTET 2025
CTET Exam 2026 Qualifying Marks
Candidates must achieve a minimum qualifying percentage to pass the CTET exam. General category candidates require at least 60% while reserved category candidates need 55%. There is no negative marking for incorrect answers. The table below presents the CTET qualifying marks for different categories.
| Category | CTET Minimum Qualifying Percentage | CTET Passing Marks (Out of 150) |
| General | 60% | 90 |
| OBC | 55% | 82 |
| SC | 55% | 82 |
| ST | 55% | 82 |
CTET Exam Pattern 2026 Mode
CTET Exam Pattern 2026 February session details in pointwise format:

CTET Syllabus 2026 Paper 1 Classes 1-5
CTET Syllabus 2026 Paper 1 is designed for candidates aiming to teach Classes 1 to 5 and covers Child Development & Pedagogy, Language, Mathematics, and Environmental Studies.
| Section | Sub-Section | Number of Questions | Topics Covered |
| I. Child Development and Pedagogy | a) Child Development (Primary School Child) | 15 | • Concept of development and its relationship with learning
• Principles of the development of children • Influence of Heredity & Environment • Socialization processes: Social world & children (Teacher, Parents, Peers) • Piaget, Kohlberg, and Vygotsky: constructs and critical perspectives • Concepts of child-centered and progressive education • Critical perspective of the construct of Intelligence • Multi-Dimensional Intelligence • Language & Thought • Gender as a social construct; gender roles, gender-bias, and educational practice • Individual differences among learners, understanding differences based on diversity of language, caste, gender, community, religion, etc. • Distinction between Assessment for learning and assessment of learning; School-Based Assessment, Continuous & Comprehensive Evaluation: perspective and practice • Formulating appropriate questions for assessing readiness levels of learners; for enhancing learning and critical thinking in the classroom and for assessing learner achievement. |
| b) Concept of Inclusive Education and Understanding Children with Special Needs | 5 | • Addressing learners from diverse backgrounds including disadvantaged and deprived
• Addressing the needs of children with learning difficulties, “impairment,” etc. • Addressing the Talented, Creative, Specially abled Learners. |
|
| c) Learning and Pedagogy | 10 | • How children think and learn; how and why children “fail” to achieve success in school performance
• Basic processes of teaching and learning; children’s strategies of learning; learning as a social activity; social context of learning • Child as a problem solver and a “scientific investigator” • Alternative conceptions of learning in children, understanding children’s “errors” as significant steps in the learning process • Cognition & Emotions • Motivation and learning • Factors contributing to learning—personal & environmental. |
|
| II. Mathematics | a) Content | 15 | • Geometry
• Shapes & Spatial Understanding • Solids around Us • Numbers • Addition and Subtraction • Multiplication • Division • Measurement • Weight • Time • Volume • Data Handling • Patterns • Money. |
| b) Pedagogical Issues | 15 | • Nature of Mathematics/Logical thinking; understanding children’s thinking and reasoning patterns and strategies of making meaning and learning
• Place of Mathematics in Curriculum • Language of Mathematics • Community Mathematics • Evaluation through formal and informal methods • Problems of Teaching • Error analysis and related aspects of learning and teaching • Diagnostic and Remedial Teaching. |
|
| III. Environmental Studies | a) Content | 15 | i. Family and Friends:
• Relationships • Work and Play • Animals • Plants ii. Food iii. Shelter iv. Water v. Travel vi. Things We Make and Do. |
| b) Pedagogical Issues | 15 | • Concept and scope of EVS
• Significance of EVS, integrated EVS • Environmental Studies & Environmental Education • Learning Principles • Scope & relation to Science & Social Science • Approaches of presenting concepts • Activities • Experimentation/Practical Work • Discussion • CCE • Teaching material/Aids • Problems. |
|
| IV. Language I | a) Language Comprehension | 15 | • Reading unseen passages—two passages: one prose or drama and one poem with questions on comprehension, inference, grammar, and verbal ability (Prose passage may be literary, scientific, narrative, or discursive). |
| b) Pedagogy of Language Development | 15 | • Learning and acquisition
• Principles of language Teaching • Role of listening and speaking; function of language and how children use it as a tool • Critical perspective on the role of grammar in learning a language for communicating ideas verbally and in written form • Challenges of teaching language in a diverse classroom; language difficulties, errors, and disorders • Language Skills • Evaluating language comprehension and proficiency: speaking, listening, reading, and writing • Teaching-learning materials: Textbook, multi-media materials, multilingual resource of the classroom • Remedial Teaching. |
|
| V. Language II | a) Comprehension | 15 | • Two unseen prose passages (discursive or literary or narrative or scientific) with questions on comprehension, grammar, and verbal ability. |
| b) Pedagogy of Language Development | 15 | • Learning and acquisition
• Principles of language Teaching • Role of listening and speaking; function of language and how children use it as a tool • Critical perspective on the role of grammar in learning a language for communicating ideas verbally and in written form • Challenges of teaching language in a diverse classroom; language difficulties, errors, and disorders • Language Skills • Evaluating language comprehension and proficiency: speaking, listening, reading, and writing • Teaching-learning materials: Textbook, multi-media materials, multilingual resource of the classroom • Remedial Teaching. |
CTET Syllabus 2026 Paper II for classes VI to VIII Elementary Stage
CTET Syllabus 2026 Paper II is meant for candidates aspiring to teach Classes 6 to 8 at the elementary stage, covering Child Development & Pedagogy, Languages, Mathematics & Science, and Social Studies/Social Science.
| Section | Sub-Section | Number of Questions | Topics Covered |
| I. Child Development and Pedagogy | a) Child Development (Elementary School Child) | 15 | • Concept of development and its relationship with learning
• Principles of the development of children • Influence of Heredity & Environment • Socialization processes: Social world & children (Teacher, Parents, Peers) • Piaget, Kohlberg, and Vygotsky: constructs and critical perspectives • Concepts of child-centered and progressive education • Critical perspective of the construct of Intelligence • Multi-Dimensional Intelligence • Language & Thought • Gender as a social construct; gender roles, gender-bias, and educational practice • Individual differences among learners, understanding differences based on diversity of language, caste, gender, community, religion, etc. • Distinction between Assessment for learning and assessment of learning; School-Based Assessment, Continuous & Comprehensive Evaluation: perspective and practice • Formulating appropriate questions for assessing readiness levels of learners; for enhancing learning and critical thinking in the classroom and for assessing learner achievement. |
| b) Concept of Inclusive Education and Understanding Children with Special Needs | 5 | • Addressing learners from diverse backgrounds including disadvantaged and deprived
• Addressing the needs of children with learning difficulties, “impairment,” etc. • Addressing the Talented, Creative, Specially abled Learners. |
|
| c) Learning and Pedagogy | 10 | • How children think and learn; how and why children “fail” to achieve success in school performance
• Basic processes of teaching and learning; children’s strategies of learning; learning as a social activity; social context of learning • Child as a problem solver and a “scientific investigator” • Alternative conceptions of learning in children, understanding children’s “errors” as significant steps in the learning process • Cognition & Emotions • Motivation and learning • Factors contributing to learning—personal & environmental. |
|
| II. Mathematics and Science | (i) Mathematics | 30 | a) Content (20 Questions):
• Number System: Knowing our Numbers, Playing with Numbers, Whole Numbers, Negative Numbers and Integers, Fractions • Algebra: Introduction to Algebra, Ratio and Proportion • Geometry: Basic geometrical ideas (2-D), Understanding Elementary Shapes (2-D and 3-D), Symmetry (reflection), Construction (using Straight edge Scale, protractor, compasses), Mensuration • Data Handling |
| b) Pedagogical Issues (10 Questions):
• Nature of Mathematics/Logical thinking • Place of Mathematics in Curriculum • Language of Mathematics • Community Mathematics • Evaluation • Remedial Teaching • Problem of Teaching. |
|||
| (ii) Science | 30 | a) Content (20 Questions):
• Food: Sources of food, Components of food, Cleaning food • Materials: Materials of daily use • The World of the Living • Moving Things People and Ideas • How things work: Electric current and circuits, Magnets • Natural Phenomena • Natural Resources |
|
| b) Pedagogical Issues (10 Questions):
• Nature & Structure of Sciences • Natural Science/Aims & objectives • Understanding & Appreciating Science • Approaches/Integrated Approach • Observation/Experiment/Discovery (Method of Science) • Innovation • Text Material/Aids •Evaluation-cognitive/psycho-motor/affective • Problems • Remedial Teaching. |
|||
| III. Social Studies/Social Sciences | a) Content | 40 | History:
• When, Where and How • The Earliest Societies • The First Farmers and Herders • The First Cities • Early States • New Ideas • The First Empire • Contacts with Distant Lands • Political Developments • Culture and Science • New Kings and Kingdoms • Sultans of Delhi • Architecture • Creation of an Empire • Social Change • Regional Cultures • The Establishment of Company Power • Rural Life and Society • Colonialism and Tribal Societies • The Revolt of 1857-58 • Women and Reform • Challenging the Caste System • The Nationalist Movement • India After Independence |
| Geography:
• Geography as a social study and as a science • Planet: Earth in the solar system • Globe • Environment in its totality: natural and human environment • Air • Water • Human Environment: settlement, transport, and communication • Resources: Types-Natural and Human • Agriculture |
|||
| Social and Political Life:
• Diversity • Government • Local Government • Making a Living • Democracy • State Government • Understanding Media • Unpacking Gender • The Constitution • Parliamentary Government • The Judiciary • Social Justice and the Marginalised. |
|||
| b) Pedagogical Issues | 20 | • Concept & Nature of Social Science/Social Studies
• Classroom Processes, activities, and discourse • Developing Critical thinking • Enquiry/Empirical Evidence • Problems of teaching Social Science/Social Studies • Sources- Primary & Secondary • Projects Work • Evaluation. |
|
| IV. Language I | a) Language Comprehension | 15 | • Reading unseen passages—two passages: one prose or drama and one poem with questions on comprehension, inference, grammar, and verbal ability (Prose passage may be literary, scientific, narrative, or discursive). |
| b) Pedagogy of Language Development | 15 | • Learning and acquisition
• Principles of language Teaching • Role of listening and speaking; function of language and how children use it as a tool • Critical perspective on the role of grammar in learning a language for communicating ideas verbally and in written form • Challenges of teaching language in a diverse classroom; language difficulties, errors, and disorders • Language Skills • Evaluating language comprehension and proficiency: speaking, listening, reading, and writing • Teaching-learning materials: Textbook, multi-media materials, multilingual resource of the classroom • Remedial Teaching. |
|
| V. Language II | a) Comprehension | 15 | • Two unseen prose passages (discursive or literary or narrative or scientific) with questions on comprehension, grammar, and verbal ability. |
| b) Pedagogy of Language Development | 15 | • Learning and acquisition
• Principles of language Teaching • Role of listening and speaking; function of language and how children use it as a tool • Critical perspective on the role of grammar in learning a language for communicating ideas verbally and in written form
• Challenges of teaching language in a diverse classroom; language difficulties, errors, and disorders • Language Skills • Evaluating language comprehension and proficiency: speaking, listening, reading, and writing • Teaching-learning materials: Textbook, multi-media materials, multilingual resource of the classroom • Remedial Teaching. |
STRUCTURE AND CONTENT OF SYLLABUS (Paper I and Paper II)
Note: For Detailed syllabus of classes l-VIII, please refer to NCERT syllabus and text books
CTET Syllabus 2026 Download
To get the CTET Syllabus 2026, visit the official CTET website ctet.nic.in and check the Information Bulletin. It contains the detailed syllabus for Paper 1 (Classes 1-5) and Paper 2 (Classes 6-8). The syllabus covers Child Development, Languages, Mathematics, Environmental Studies (Paper 1), and Science/Social Studies (Paper 2). According to sources like Jagran Josh and Shiksha, the PDFs will be available from late November 2025.
Where to Download
- Official Website: ctet.nic.in – look for the Information Bulletin.
- Educational Portals: Sites like JRFAdda
Syllabus Overview
- Paper 1 (Primary Stage – Classes 1-5): Child Development & Pedagogy, Language I & II, Mathematics, Environmental Studies (EVS).
- Paper 2 (Elementary Stage – Classes 6-8): Child Development & Pedagogy, Language I & II, Mathematics & Science, or Social Studies/Social Science.
Key Points to Remember
- Both papers consist of 150 multiple-choice questions, each carrying 1 mark, with no negative marking.
- The syllabus is primarily based on the NCERT curriculum for the respective classes, so focusing on NCERT books is highly recommended.
CTET Exam Pattern 2026 Conclusion
The CTET 2026 exam follows a structured pattern to assess candidates’ teaching aptitude and subject knowledge. Paper 1 is for classes 1–5, and Paper 2 is for classes 6–8. Each paper has 150 multiple-choice questions, 1 mark each, with no negative marking. The exam is offline, available in English and Hindi, and evaluates conceptual understanding, problem-solving, and pedagogical skills. Knowing the pattern helps candidates plan preparation effectively, focus on key topics, and attempt questions with confidence.
CTET Exam Pattern 2026 FAQs
CTET Exam Pattern 2026 FAQs
CTET 2026 will be conducted offline using pen-and-paper (OMR sheets).
CTET 2026 will be conducted offline using pen-and-paper (OMR sheets).
There are two papers: Paper 1 for classes 1–5 and Paper 2 for classes 6–8.
What are the subjects in Paper 2?
Paper 2 covers Child Development & Pedagogy, Language I & II, Mathematics & Science or Social Studies.
How can I prepare according to the CTET 2026 exam pattern?
Follow the syllabus, practice NCERT questions, solve past papers, and take mock tests.